Failure Analysis Software
Failure Analysis Methods, Tools and Services
Failure analysis is the process of collecting and analyzing data to determine the cause of a failure and how to prevent it from recurring. It is an important discipline in many branches of manufacturing industry, such as the electronics industry, where it is a vital tool used in the development of new products and for the improvement of existing products. It is especially important in manufacturing and field use of safety-critical and mission-critical equipment.
Failure analysis may be applied to both products and processes.
Failure analysis may be conducted on the design stage and on field use stage of the product life cycle.
Failure analysis may be conducted on the design stage and on field use stage of the product life cycle.
There are several different failure analysis methods and tools:Failure Data Collection
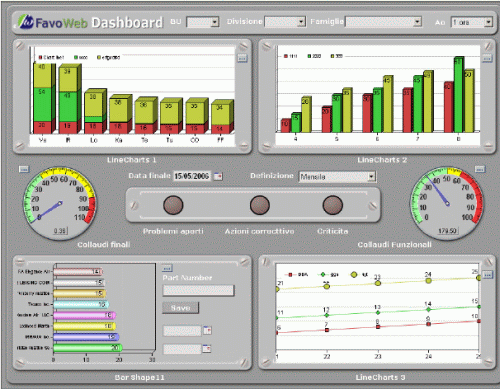
Failure analysis of safety-critical and mission-critical equipment on the field use stage requires failure data collection and statistical analysis. To accomplish this goal special software system called FRACAS (Failure Reporting, Analysis and Corrective Actions System) should be used. Collected data are subject to statistical analysis. Such system also gives real-time added value for the organization and acts like fleet management system, safety management system, workflow system with alerts and escalation and more.
Collected statistics and obtained field failure rates could be used in all failure analysis methods mentioned below.
Collected statistics and obtained field failure rates could be used in all failure analysis methods mentioned below.
FMECA
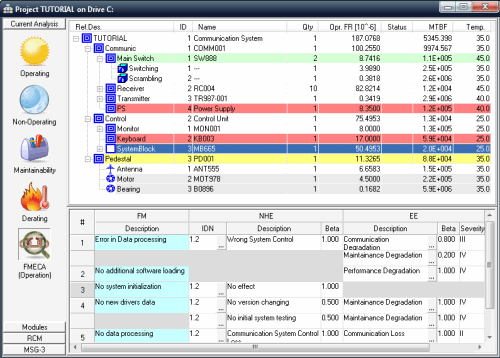
Hardware FMEA and FMECA (Failure Mode, Effects and Criticality Analysis) is a continuation of system reliability analysis. It is required and compatible with MIL-STD-1629A and other standards (like GJB 1391, GJB 1392, AIR FORCE SMC REGULATION 800-31 and more). Many standards and regulations for aerospace, defence, telecommunications, electronic and other industries require that FMECA analysis must be performed for all designed/manufactured/acquisition systems, especially if they are mission or safety critical.
FMECA includes failure analysis, criticality analysis and testability analysis. It analyzes different failure modes and their effects on the system, classifies and prioritizes end effects level of importance based on failure rate and severity of the effect of failure.
FMECA includes failure analysis, criticality analysis and testability analysis. It analyzes different failure modes and their effects on the system, classifies and prioritizes end effects level of importance based on failure rate and severity of the effect of failure.
FMEA
Potential FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) is analytical technique utilized as a mean to assure that, to the extent possible, potential failure modes and their associated causes/mechanisms have been considered and adressed. Corrective actions are suggested and selected for implementation and control plan is formed as part of the procedure.
Potential Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) complies with AIAG, QS-9000, SAE J 1739, IEC 60812, JEP131 and other standards, sometimes called “automotive” or “AIAG” (Automotive Industry Action Group) FMEA. It is required by many other standards like ISO 14971 (Medical devices risk management) and more.
Potential Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) complies with AIAG, QS-9000, SAE J 1739, IEC 60812, JEP131 and other standards, sometimes called “automotive” or “AIAG” (Automotive Industry Action Group) FMEA. It is required by many other standards like ISO 14971 (Medical devices risk management) and more.
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
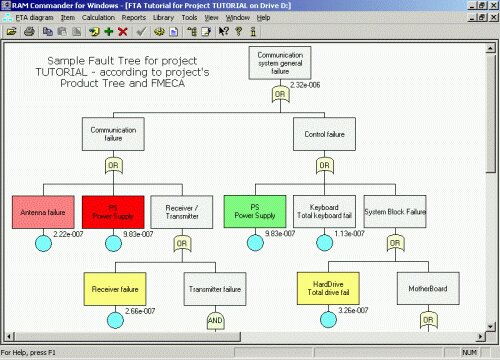
Fault Trees are one of the most widely used methods in system reliability and failure probability analysis. A Fault Tree is a graphical representation of events in a hierarchical, tree-like structure. It is used to determine various combinations of hardware, software, and human error failures that could result in a specified risk or system failure. System failures are often referred to as top events. A deductive analysis using a Fault Tree begins with a general conclusion or hazard, which is displayed at the top of a hierarchical tree. This deductive analysis is the final event in a sequence of events for which the Fault Tree is used to determine if a failure will occur or, alternatively, can be used to stop the failure from occurring.
Fault Trees investigate consequences of multiple simltaneous failures or events, and here its main advantage over FMEA/FMECA, which investigate single-pint failures.
Fault Trees investigate consequences of multiple simltaneous failures or events, and here its main advantage over FMEA/FMECA, which investigate single-pint failures.
Event Tree Analysis (ETA)
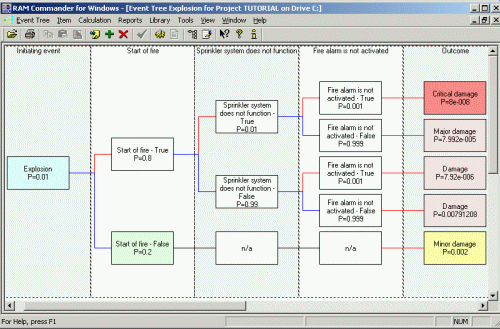
It is an inductive failure analysis performed to determine the consequences of single failure for the overall system risk or reliability. Event Tree Analysis uses similar logic and mathematics as Fault Tree Analysis, but the approach is different – FTA uses deductive approach (from system failure to it’s reasons) and ETA uses the inductive approach (from basic failure to it’s consequences).
An event tree itself is a visual representation of single failure sequences, it’s influence on other events and on the whole system.
An event tree itself is a visual representation of single failure sequences, it’s influence on other events and on the whole system.